Kinh Nghiệm về Serious requests that ask the supplier to specify pricing and terms are called Chi Tiết
Hoàng Quang Hưng đang tìm kiếm từ khóa Serious requests that ask the supplier to specify pricing and terms are called được Update vào lúc : 2022-12-15 08:40:13 . Với phương châm chia sẻ Bí quyết về trong nội dung bài viết một cách Chi Tiết 2022. Nếu sau khi đọc tài liệu vẫn ko hiểu thì hoàn toàn có thể lại Comments ở cuối bài để Tác giả lý giải và hướng dẫn lại nha.Supplier relationship management (SRM) is the systematic approach to evaluating vendors that supply goods, materials and services to an organization, determining each supplier's contribution to success and developing strategies to improve their performance.
Nội dung chính Show- Guide to supply chain managementGoals of supplier relationship managementTasks of supplier relationship managementSupplier relationship management processSRM use casesSRM challengesSRM softwareHistory of SRMWhat does sourcing mean in business?What are the most common sources of supply information?What is the final step in the supplier selection and evaluation process?Which of the following is the first stage of supplier selection?
The SRM discipline helps to determine the value each supplier provides and which ones are most critical to business continuity and performance. It also enables managers to cultivate better relationships with suppliers based on each supplier's importance.
Supplier relationship management is used by supply chain professionals who regularly giảm giá with suppliers in areas such as procurement, project management and operations.
Sometimes called supply chain relationship management, SRM is one of the many disciplines of supply chain management. It is similar to vendor management and procurement processes, but there are key differences. Vendor management generally focuses on establishing costs and service-level agreements between the organization and its vendors, while procurement focuses on the purchase itself (i.e., ordering, contracting, invoicing and paying).
This article is part of
Guide to supply chain management
- Which also includes:5 potential benefits of blockchain in supply chain logisticsThe supply chain sustainability software market demystifiedTop 5 inventory management challenges for manufacturers
Download1
Download this entire guide for FREE now!
Goals of supplier relationship management
Although different industries have differing categories of critical suppliers and each organization has its own unique mix, the overarching goal of SRM remains the same: to streamline and improve the processes that take place between the organization as buyer of products and services and the businesses that supply them.
Similar to the way that customer relationship management (CRM) is intended to streamline and improve the processes between an enterprise and its customers, SRM aims to develop a mutually beneficial relationship between the organization and its suppliers, especially those deemed most strategic to the organization's brand. It is also meant to promote quality, efficiency and innovation. A successful SRM discipline seeks not just cost savings, but to maximize the value of suppliers to gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Supplier relationship management has become increasingly important as buyer-supplier networks become more global and interdependent and companies rely more heavily on strategic suppliers. SRM creates a framework for both identifying the strategic supply partners and organizing the relationship lifecycle. Its practices create a common frame of reference to enable effective communication between an enterprise and suppliers and measure supplier performance.
Some suppliers are more critical to business continuity, operational excellence, scalability and ultimately profitability. For example, a smartphone manufacturer's stationery supplier has little influence on profitability, but its main electronics supplier has a huge impact, making it a key strategic partner. Any risk to the electronics maker's operations is a major risk to the smartphone company.
Tasks of supplier relationship management
To achieve its goals, an organization's SRM program must be strategic in approach -- articulating objectives and devising a plan before addressing suppliers -- rather than being reactive and engaging suppliers on an ad hoc basis or in response to particular issues.
Enterprise leaders who take a strategic approach, for example, might determine that long-term engagements with specific suppliers are preferable to ensure continuity of supplies, while short-term relationships with other suppliers can best ensure business agility and flexible pricing.
An effective SRM strategy also requires cultivating personal relationships with suppliers and working to build trust and mutually beneficial partnerships when appropriate. That could mean involving them in planning for key initiatives or jointly developing innovations.
Leaders involved in SRM must also work to align everyone in their organization with the goals of the SRM program and ensure compliance with its objectives. They should also have a process for determining the value that the SRM program returns to the organization.
Supplier relationship management process
The processes of strategic sourcing related to SRM can vary from one organization to the next. However, SRM generally involves three broad steps:
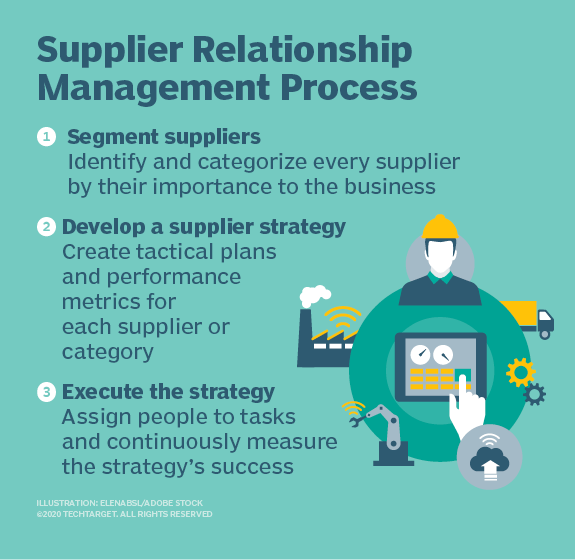
- Segment suppliers. In this first, foundational step, the organization identifies all of its suppliers and categorizes them by their importance to the business, thereby ensuring that the suppliers most critical to success get the right amount of attention.Develop a supplier strategy. In this step, the organization develops a tactical plan for how it will work with each supplier or category of suppliers to ensure the relationships are successful and mutually beneficial. Organizations should start with the category of suppliers deemed most critical but recognize that all suppliers play a role in success and thus also merit a strategic approach that involves governance and performance management models to align business processes and assign stakeholders according to business goals.Execute the supplier strategy. The executives who own the SRM discipline in the organization need to ensure that the strategy is put into action and that they or managers take on day-to-day tasks to operationalize the SRM plans. They should also devise ways to monitor and measure SRM success as well as identify deficiencies and points of failure in the SRM strategy or its execution.
SRM use cases
Organizations have reported numerous use cases for implementing SRM, noting that the discipline helps them to:
- take better advantage of supplier capabilities;reduce costs;ensure supply chain continuity;limit supply chain risks;increase responsiveness of suppliers; andgain visibility into future prices and hedge against price volatility.
Consider the findings in a case study published by State of Flux, a management consulting company that specializes in global procurement and supply chains. The United States Postal Service decided to update its SRM governance model in 2022, even though its SRM was already considered mature. The USPS streamlined its supplier rating system from nine down to four standard metrics for timeliness, quality, cost and innovation that are applied to every supplier. The relationship managers assigned to individual suppliers have flexibility, however, to add optional metrics for factors such as corporate social responsibility or the quality of specific product categories like software. Suppliers have input into the SRM process through several mechanisms, including membership on a supplier council.
SRM challenges
A 2022 survey of 715 supply chain decision-makers for a report, "Supply chain resilience in a post-pandemic world," by Jabil, a manufacturing services company, and Dimensional Research found that 70% of respondents experienced disruptions due to the COVID-19 pandemic, while 44% indicated supply constraints and 35% faced global trade and tariff issues. Moreover, 95% of respondents said their company was affected by component shortages.
Such findings speak to the importance of having a solid SRM program, yet other research also points out the many challenges in achieving that objective.
Challenges that can stymie supplier relationship management include the following:
- overemphasis on using it to reduce cost rather than cultivate value and strategic ties;lack of visibility into suppliers, their importance to the organization and the value they can deliver; andinsufficient commitment to developing clear objectives for the program, assigning and training staff to run it, and aligning business units to the objectives.
SRM software
SRM software offers a variety of functions that enable a strong supplier management operation, including the following key features and capabilities:
- contact and communication management;invoices and requisitions;order histories;scheduling;performance analytics;procurement intelligence, including supplier risk management;product lifecycle management, such as portfolio strategy management;sourcing;supplier data management, including validating supplier requests;supplier performance management;contract management;catalog management;operational procurement, such as processing purchase orders; andexternal resources, such as product specifications.
SRM software vendors include Coupa, GEP Software, Intelex, SAP (including SAP Ariba) and Taulia.
History of SRM
The emergence of supplier relationship management is credited to Peter Kraljic, a director the consulting firm McKinsey & Company. In an article titled "Purchasing Must Become Supply Management" published in the September 1983 Harvard Business Review, he discussed segmenting the supplier base and mapping it against two key dimensions: risk and profitability. Kraljic wrote that for organizations to giảm giá with the risks, complexities and potential supply and pricing disruptions "management must learn to make things happen to its own advantage. This calls for nothing less than a total change of perspective: from purchasing (an operating function) to supply management (a strategic one)." Others built on Kraljic's core idea to develop SRM, and the discipline has continued to evolve as technologies and processes change and mature.
What does sourcing mean in business?
Sourcing is the process of vetting, selecting, and managing suppliers who can provide the inputs an organization needs for day-to-day running. Sourcing is tasked with carrying out research, creating and executing strategy, defining quality and quantity metrics, and choosing suppliers that meet these criteria.What are the most common sources of supply information?
The sources of information regarding the potential suppliers are:. Newspaper advertisements.. Trade directories.. Catalogue, price lists etc.. Trade journals.. Salesmen.. Advertised tender.. Telephone directories.. Exchange of information between similar companies..What is the final step in the supplier selection and evaluation process?
Selecting suppliers is the final step of the supplier selection and evaluation process.Which of the following is the first stage of supplier selection?
First Stage: Evaluating Offers Evaluating a supplier's offer includes not only evaluating its bit but also checking out the supplier's ability to perform to the required level of speed and quality. Evaluate offers in terms of both: potential risk and benefits. Tải thêm tài liệu liên quan đến nội dung bài viết Serious requests that ask the supplier to specify pricing and terms are called